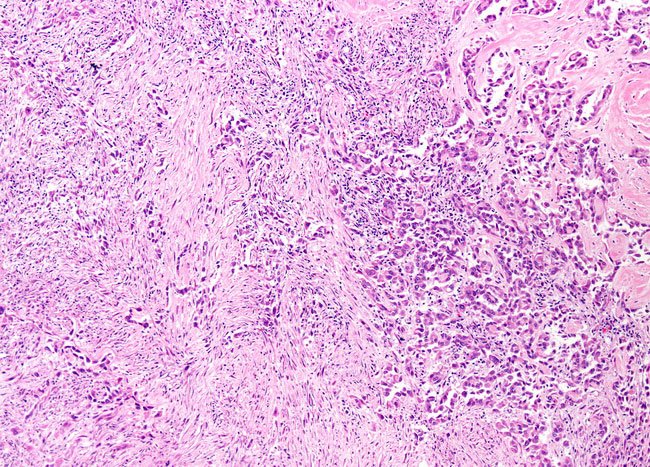
This cancer type is also identified based on the cancer cell type: epithelioid, sarcomatoid, and biphasic.
Mesothelioma is a terminal cancer that is classified in four types, based on tumor location: pleural, peritoneal, pericardial, and testicular.
The symptoms and treatment options will differ based on the type of mesothelioma and severity.

Mesothelioma Based on Location
Pleural Mesothelioma
The most common form of mesothelioma is pleural mesothelioma. This cancer type affects the pleura, which is the thin lining around the lungs. Around 70% to 75% of mesothelioma cases are classified as pleural mesothelioma. Given that this is the most common type of mesothelioma, the most research has been done on this form.

Symptoms
Since pleural mesothelioma primarily affects the lungs, symptoms most often include shortness of breath and chest pain. Weight loss, fever, and fatigue are also common symptoms of pleural mesothelioma.
Prognosis
If caught early on, the life expectancy for someone with stage one pleural mesothelioma will be 3 or more years. In contrast, someone with stage four pleural mesothelioma typically has a life expectancy of less than 12 months. The severity of the cancer and other factors will affect the exact prognosis.
Treatment
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are the most common treatment options for those with pleural mesothelioma. Some patients may also qualify for immunotherapy or clinical trials. These treatments will diminish the symptoms and hopefully decrease the size of the tumor, resulting in an increased quality of life and life expectancy.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma
The second most common form of mesothelioma is peritoneal mesothelioma, meaning that it affects the abdomen. About 10% to 20% of mesothelioma cases classify as peritoneal mesothelioma. Given that this type of cancer is much rarer than pleural mesothelioma, less research has been conducted on it. Still, the prognosis for this cancer is often better.

Symptoms
Peritoneal mesothelioma often has symptoms relating to the abdomen. This can include abdominal pain, swelling, bloating, bowel changes, and loss of appetite. Many people also have severe and unexplained weight loss as a result.
Prognosis
The prognosis for peritoneal mesothelioma is much higher than pleural mesothelioma. Over half of patients live more than five 5 after surgery and treatment with HIPEC.
Treatment
Peritoneal mesothelioma is often treated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Just using traditional chemotherapy and radiation are typically not successful with these patients, which is why surgery is an optimal treatment strategy.
Pericardial Mesothelioma
Pericardial mesothelioma is a type of rare cancer that affects the heart. This type of cancer is extremely rare, with only around 200 cases reported in total. The prognosis for pericardial mesothelioma is traditionally very short, though some patients can live much longer than the projected life expectancy.
Symptoms
The symptoms for pericardial mesothelioma often affect the heart given that the cancer affects the heart’s lining. Chest pain, cough, difficulty breathing, and irregular heartbeat are the biggest symptoms of pericardial mesothelioma.
Prognosis
The prognosis for pericardial mesothelioma is very poor. Most patients only live between 6 weeks and 15 months after their initial diagnosis.
Treatment
Chemotherapy and palliative treatment are the most common treatment options for pericardial mesothelioma. Radiation is typically not used for this type of cancer because of how risky it is to administer around the heart.
Testicular Mesothelioma
Of the four types of mesothelioma, testicular mesothelioma is the rarest. This cancer type develops around the lining of the testes. There are less than 100 cases reported.
Symptoms
Testicular mesothelioma symptoms typically include scrotal swelling and painless testicular lumps.
Prognosis
This form of cancer, although very rare, tends to have a better prognosis than some of the other forms. Most people who are diagnosed with testicular mesothelioma live for more than 2 years after the initial diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment options for testicular mesothelioma often include surgery and chemotherapy.
Epithelial Cell Mesothelioma
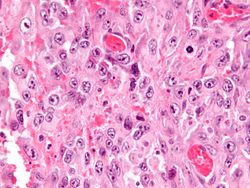
About 70% to 75% of asbestos related mesothelioma involves epithelioid mesothelioma. Generally, this diagnosis leads to the best prognosis because these cells are less aggressive and respond to treatment better. About half of pleural disease relates to epithelioid cells, while three fourths of peritoneal tumors are made up of epithelioid cells.
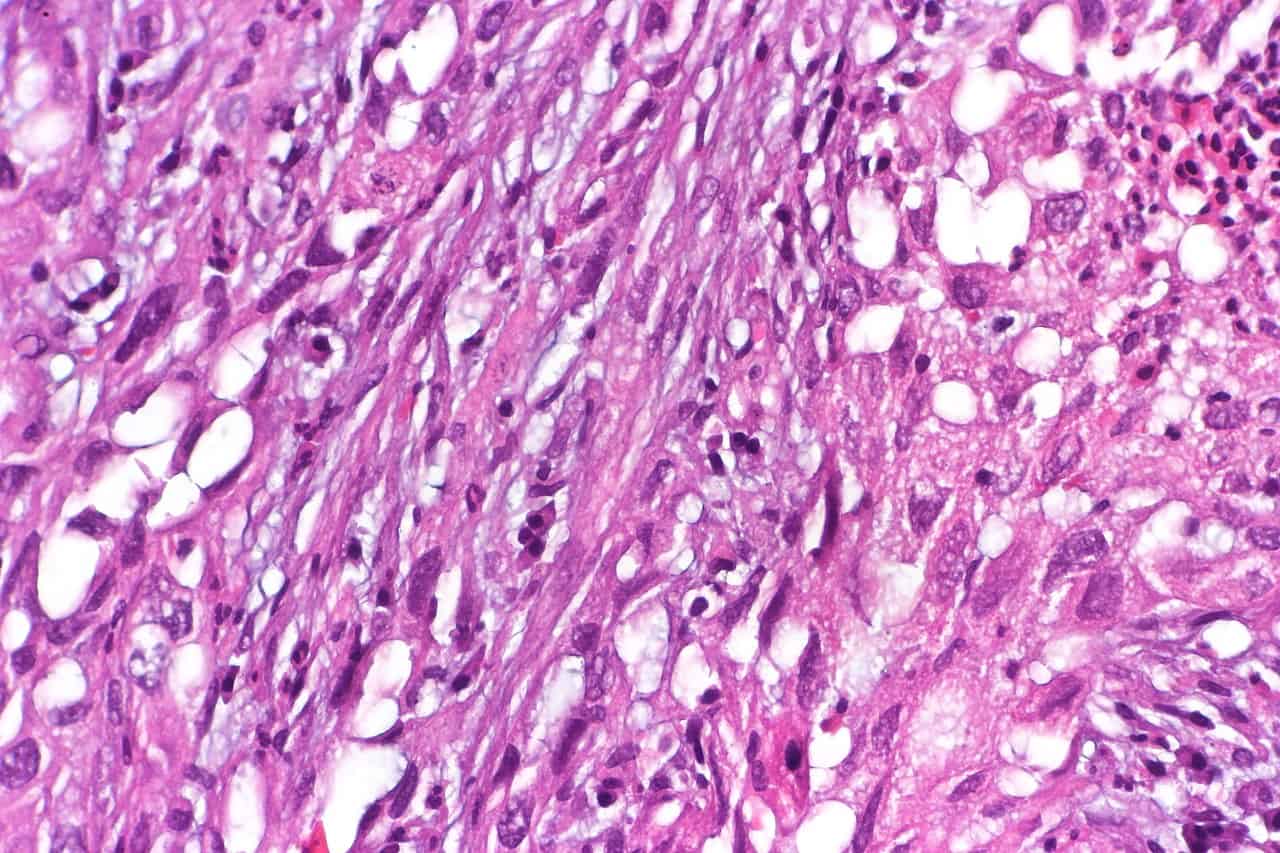
Sarcomatoid Cell Mesothelioma
Of the three cell types, sarcomatoid cells are the least common. They are the most aggressive and hardest to treat. 10% to 20% of diagnosed mesothelioma involve sarcomatoid cell mesothelioma. Around 20% of pleural tumors are made up of sarcomatoid cells, but only 1% peritoneal tumors are sarcomatous.
Biphasic
Biphasic tumors contain both epithelial and sarcomatoid cells. The life expectancy of patients diagnosed with these tumors depends on which of the two cells are most common in the tumor. More epithelioid cells result in a better prognosis since they are less aggressive and easier to treat. 30% of pleural tumors and 25% of peritoneal tumors include biphasic cells.
Other Rare Mesothelioma Cell Types
There are rare forms of mesothelioma cell types that are typically considered subtypes of the previously three mentioned cell types. Often, rare cell types lead to a difficult diagnosis and they affect the prognosis and life expectancy differently.
Below is a list of rare forms of mesothelioma cell types:
-
Adenomatoid
-
Cystic and papillary cells
-
Deciduoid mesothelioma
-
Desmoplastic and lymphohistiocytoid
-
Heterologous cells
-
Small cell mesothelioma
-
Well-differentiated papillary cells
Treatment
Treatment for mesothelioma will depend on location, cell type, cancer stage, overall health of the patient, and age. Doctors will also consider your desires and needs before treatment. Chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy are available for almost all patients, regardless of the severity or age of the cancer. For younger or early stage patients, surgery may also be recommended alongside the other treatment options.
 Rae Steinbach
Rae Steinbach